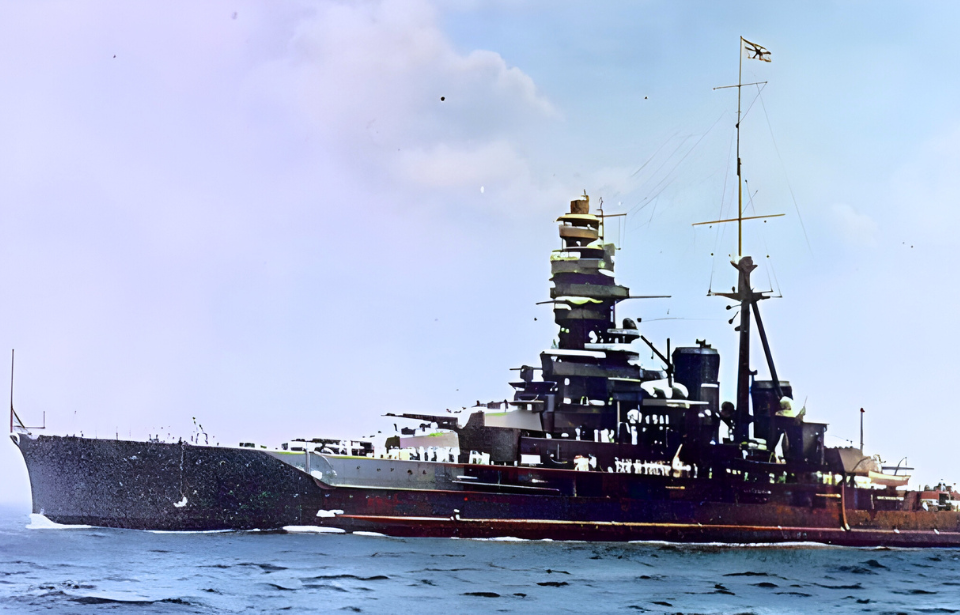
The Japanese battleship Kongō earned legendary status for its formidable strength and resilience, inspiring evocative nicknames such as “Indestructible Diamond,” “Indra’s Spear,” and “Divine Thunder.” Its service spanned both World War I and World War II, seeing action in pivotal Pacific engagements including the battles of Midway, Guadalcanal, and Leyte Gulf.
Distinguished by its remarkable speed, heavy firepower, and durable construction, Kongō stood out among contemporaneous warships, cementing its place as an enduring emblem of Japan’s naval might and the indomitable spirit of its fleet.
Construction of Kongō
Kongō was loaded with armaments
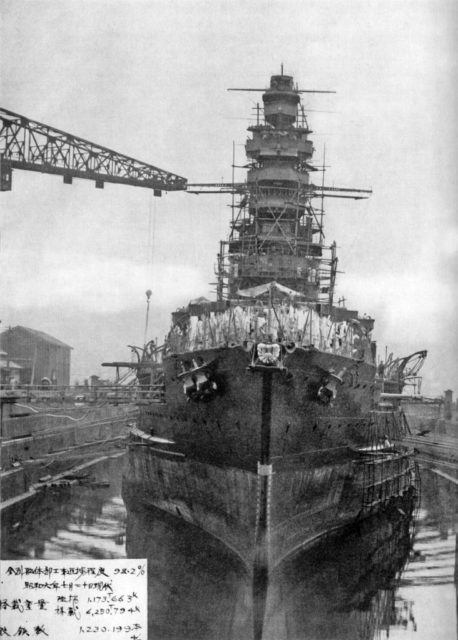

The battleship Kongō had eight 14-inch naval guns set in four twin turrets. These were the first guns of their kind to be installed on a warship and could fire both armor-piercing and high-explosive shells. The Japanese military relied heavily on Kongō’s powerful guns to gain an edge in battle, and her firepower was a big part of that strategy.
In addition to her main guns, Kongō was armed with 16 six-inch .50-caliber guns in single casemates, eight three-inch guns, and eight underwater 21-inch torpedo tubes. In 1929, she was upgraded and reclassified from a cruiser to a battleship. By October 1944, her secondary weapons had been updated to include eight six-inch guns, 122 Type 96 rapid-fire anti-aircraft cannons, and eight five-inch guns.
Service during World War I

Kongō was formally commissioned in August 1913 as a battlecruiser, and it didn’t take long for her to be pressed into service. At the outset of the First World War, she was sent to patrol German lines of communication at sea, before supporting Japanese units during the Siege of Tsingtao. Following the British defeat of Germany at the Battle of the Falkland Islands, there was little need for Kongō. As such, she was either kept at Sasebo Naval Base or on patrol near China for the remainder of the conflict.
Following WWI, world powers didn’t want to see another conflict and the Washington Naval Treaty was signed, placing restrictions on the building of new naval ships. This led to a decrease in the size of the Japanese Navy.
Interwar period and the start of World War II
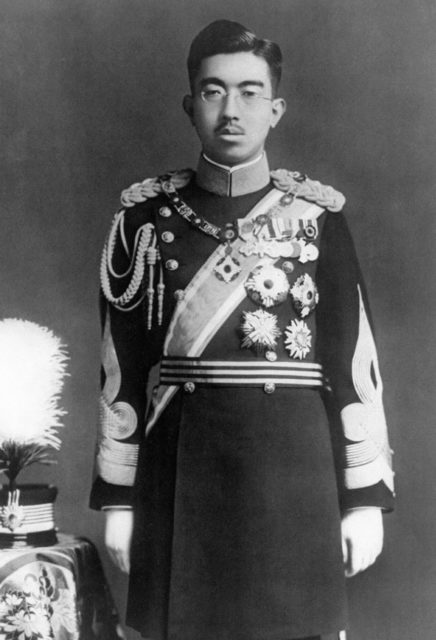

In 1923, Kongō had the honor of carrying Crown Prince Hirohito, who would later ascend to the throne as Emperor, on an official visit to Taiwan. During the years leading up to World War II, the battleship underwent significant upgrades. Starting in 1929, the Japanese Empire began transforming Kongō from a cruiser into a fully-fledged battleship, a transformation completed by 1935. The ship’s speed was enhanced, and its armor, particularly around the ammunition magazines, was strengthened to better withstand enemy fire.
Kongō was actively engaged during the Second Sino-Japanese War, where it participated in bombing raids on the Chinese town of Fuzhou. When the Second World War erupted, Kongō was deployed to the Pacific theater.
On February 22, 1942, Kongō played a role in the Japanese invasion of the Dutch East Indies. Over the course of that year, the battleship took part in numerous naval engagements, sinking several British Empire ships as part of Japan’s campaign in the Pacific.
The loss of Kongō in the Formosa Strait

For Kongō and Japan, the start of the Pacific campaign went very well. However, the tides turned during the Battle of Midway with the loss of four of the Combined Fleet’s aircraft carriers. The ship also took part in the Guadalcanal Campaign, during which Henderson Field was bombarded with high-explosive shells in what was the most successful Japanese battleship action of the Second World War.
The next two major offensives the vessel took part in were the battles of the Philippine Sea and Leyte Gulf. Kongō played an important role in Leyte Gulf, sinking multiple American vessels, including the destroyer escort USS Samuel B. Roberts (DE-413). Despite this, the battle resulted in a victory for the Allies.
Not long after, in November 1944, Kongō was spotted by the submarine USS Sealion (SS-315) in the Formosa Strait. The vessel fired six bow torpedoes at the battleship, two of which hit and flooded Kongō‘s boiler rooms. While she was able to escape the scene, the damage proved to be too much, with her sinking to the bottom of the strait after her forward 14-inch magazine exploded. Over 1,200 crewmen died.
More from us: Only 10 Crewmen Survived the Sinking of the Japanese Battleship Fusō – Out of 1,600
Kongō was the only Japanese battleship to be sunk by a submarine during WWII, while Sealion was the only Allied submarine to sink an enemy battleship.
