In 1965, U.S. Army soldier Charles Robert Jenkins made a fateful choice: he deserted his post and crossed the border into North Korea, hoping to escape deployment to Vietnam. What he anticipated as a brief reprieve turned into nearly forty years of confinement. During that time, the North Korean regime used him as a propaganda instrument, severely restricting his personal freedom.
Jenkins did not leave North Korea until 2004, when he finally reunited with his family in Japan. Upon surrendering to U.S. military authorities, he faced a court-martial for desertion, closing one extraordinary chapter of his life and beginning another shaped by reflection, endurance, and eventual reconciliation.
Charles Robert Jenkins enlisted when he was 15 years old
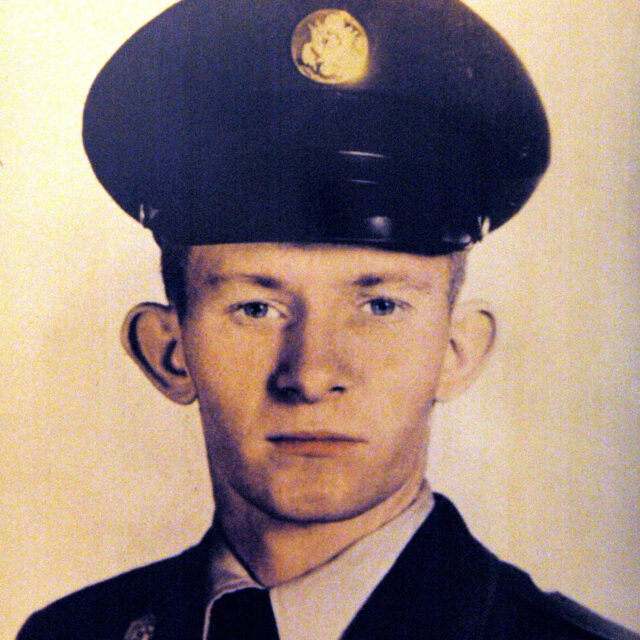
Charles Robert Jenkins entered the world on February 18, 1940, in Rich Square, North Carolina. His early years were marked by a sports injury and the passing of his father, which contributed to him not completing his education at Rich Square High School.
Lacking a high school diploma, Jenkins found his job prospects restricted. As a result, this led him to enlist in the North Carolina National Guard, serving from 1955 to 1958, which covered the majority of his teenage years.
Joining the US Army

Following an honorable discharge, Jenkins rejoined the Army at 18 and was posted to Fort Hood, Texas (now known as Fort Cavazos), where he trained as an infantryman specializing in light weapons. His career progressed with a volunteer deployment to South Korea, serving with the 7th Infantry Division from August 1960 to September 1961. Afterward, he was transferred to the 3rd Armored Division in West Germany, where he remained on duty until 1964.
Deserting the US Army
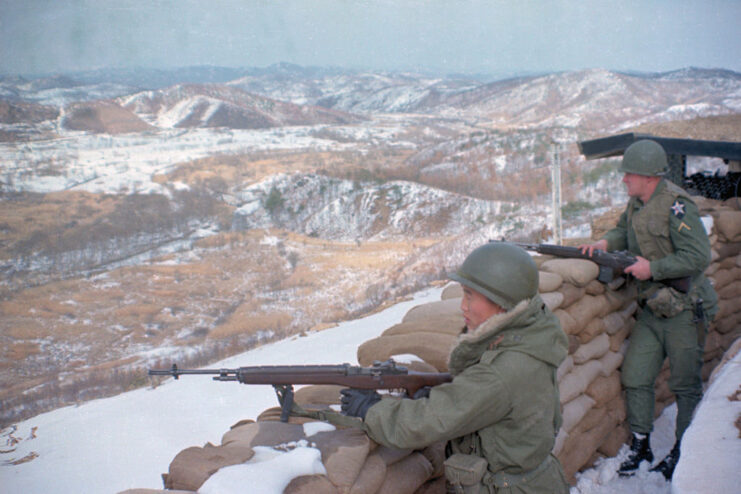

In 1964, Charles Robert Jenkins opted for a second tour in South Korea, where he served in the Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ). During this time, he was assigned to the 8th Cavalry Regiment of the 1st Cavalry Division.
On January 5, 1965, Jenkins made a decision that would alter the course of his life forever. Facing rumors that his regiment might be deployed to Vietnam and experiencing increasingly tense patrols, the sergeant crossed the DMZ into North Korea. His plan was to seek asylum with the Soviets, hoping they would facilitate his return to the United States through a prisoner exchange.
Crossing the Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)

On the night of his desertion, Charles Jenkins put away 10 beers before heading out on patrol with fellow soldiers. Around 2:30 AM, he told them he was going to investigate a suspicious noise—an excuse to slip away. As he neared the Demilitarized Zone, he removed the ammo from his M14 rifle and fastened a white T-shirt to the barrel as a makeshift flag of surrender.
Believing he’d be returned to the U.S. in short order, Jenkins crossed into North Korea. Instead, he was immediately detained, interrogated, and held captive for the next 39 and a half years.
Immediately regretting his decision
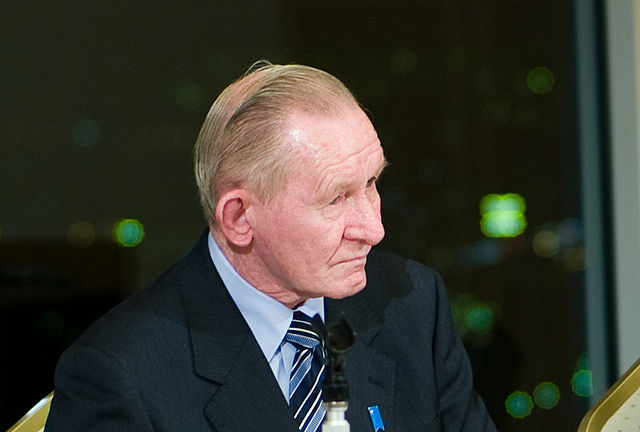

It wasn’t long after his capture and detention that Charles Robert Jenkins regretted his decision to defect to North Korea; it was not the experience he’d expected it to be.
In a 2006 interview with British publication The Independent, he called his desertion “the biggest mistake I ever made,” and in his 2008 memoir, The Reluctant Communist: My Desertion, Court-Martial and 40-Year Imprisonment in North Korea, wrote that he hadn’t realized the nation was essentially a giant “prison.”
He also explained his mindset at the time, writing, “I was not thinking clearly. But at the time my decisions had a logic to them that made my actions seem almost inevitable.”
Word of Charles Robert Jenkins’ defection spreads
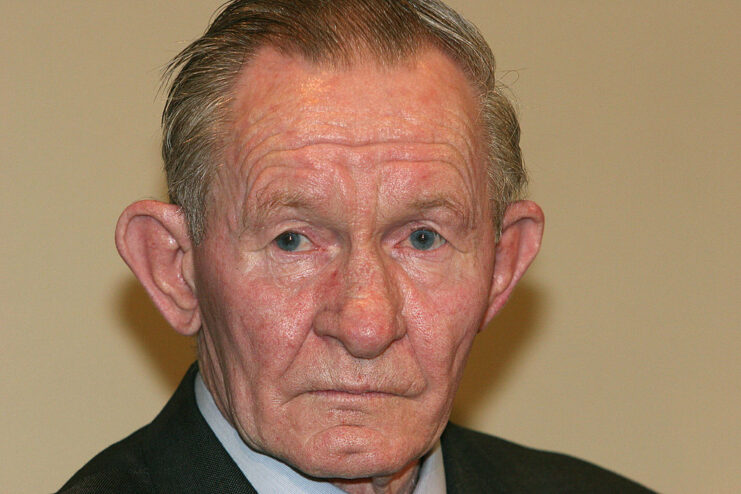

Just under two weeks after crossing the DMZ, Charles Robert Jenkins’ defection was announced on North Korean radio, which stated his decision was “because of disgust with conditions in South Korea and that he believed life was better under the Communists.”
The United States confirmed him to be a deserter based on four letters he’d sent to his mother, one of which read, “Forgive me, for I know what I must do. Tell my family I love them. Love, Charles.”
Charles Robert Jenkins was housed with other defectors

Jenkins was housed with three other American deserters while under the regime’s watchful eye:
- James Dresnok, who defected in August 1962.
- Larry Abshier, who crossed the DMZ in May 1962.
- Jerry Parrish, who deserted his post in 1963.
The conditions the four were held in were horrible; they shared one room and were beaten when they failed to properly memorize the works of Kim Il-Sung. While the group had decided to cross over into North Korea, they hadn’t necessarily planned to remain. In 1966, they attempted to follow Jenkins’ original plan to seek asylum through the Soviet embassy, but they were unsuccessful.
Working for the North Koreans

Years later, the four men were granted citizenship, provided with homes and jobs, and eventually given wives. However, despite these changes, their living conditions remained much the same. Charles Robert Jenkins later wrote that he “suffered from enough cold, hunger, beatings, and mental torture to frequently make me wish I was dead.”
Even though they were officially considered “citizens,” their captors still didn’t trust them. Their homes were bugged and surrounded by barbed wire to prevent any escape attempts. The men were also forced to act in propaganda films, playing the roles of villainous Americans. Jenkins was assigned to teach English to North Korean spies and soldiers, but his thick Southern accent eventually led to his removal from the job.
Charles Robert Jenkins marries Hitomi Soga
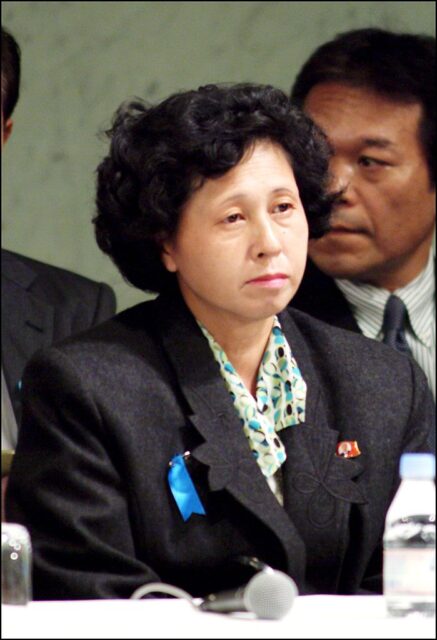

In 1980, Charles Robert Jenkins was introduced to Hitomi Soga, a Japanese nurse who’d been kidnapped a few years earlier to serve as a teacher for North Korean spies. Their union was forced, with the ceremony taking place just weeks after they first met.
Despite the lack of choice in the matter, the two developed a deep bond. Jenkins later told The Independent, “When I met her, my life changed a lot. Me and her together—I knew we could make it in North Korea. And we did.”
Over the next five years, they had two daughters, Mika (1983) and Brinda (1985).
Hitomi Soga attempts to free her husband
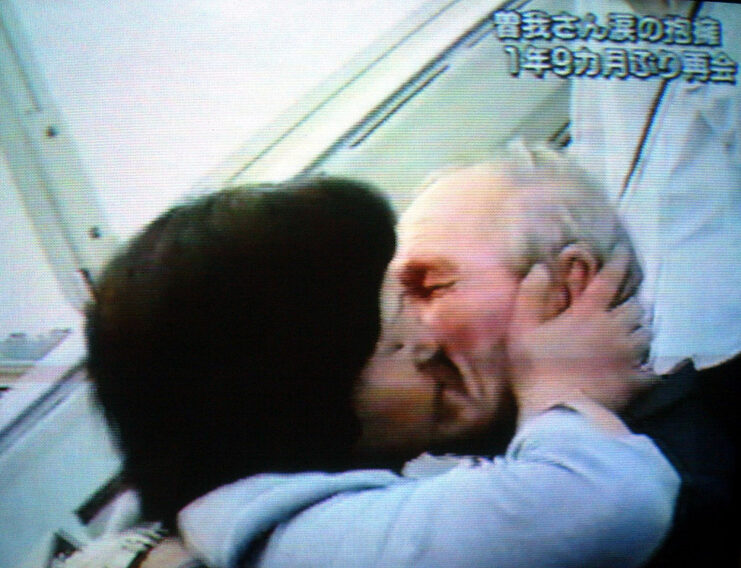

Charles Robert Jenkins’ eventual departure from North Korea was largely due to the persistent efforts of his wife, Hitomi Soga. In 2002, after the Japan-North Korea Pyongyang Declaration, Soga and four other abductees were permitted to travel to Japan for what was intended to be a ten-day visit. Rather than returning, she chose to remain in Japan and worked with government officials to try to secure a pardon for Jenkins from the United States, though her efforts were unsuccessful.
At the time, had Jenkins joined Soga in Japan, he would have faced prosecution by the U.S. military for desertion. The statute of limitations was forty years, and he had been absent for roughly thirty-nine and a half. Fearing the possibility of a death sentence, Jenkins made the heartbreaking choice to remain in North Korea with their daughters.
Charles Robert Jenkins is finally freed
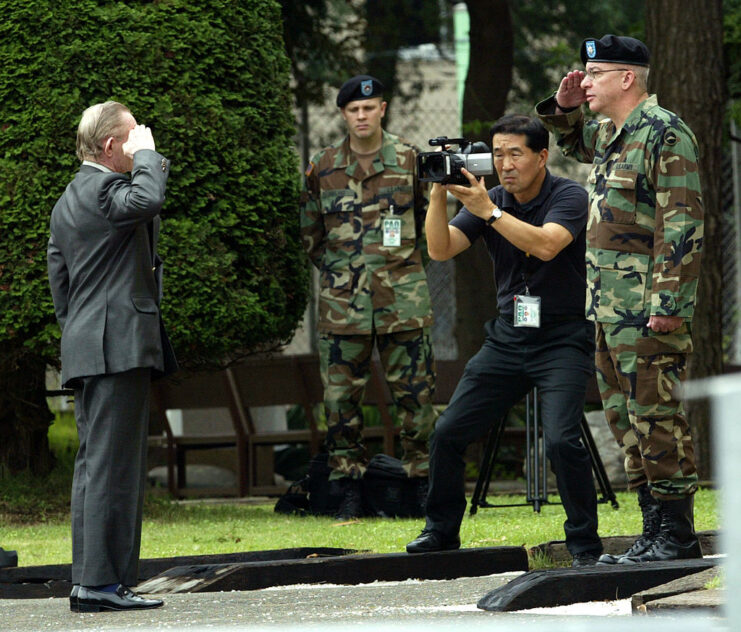

Eventually, North Korea allowed Charles Robert Jenkins to leave, and he reunited with his wife in Indonesia. That made him the only post-Korean War American defector to ever leave the restrictive country. The evidence of his mistreatment was obvious. He was 100 pounds, had lost his appendix and a testicle, and part of his US Army tattoo had been cut off without proper anesthesia.
Although Japan had promised Hitoma Soga, Jenkins and their daughters residency, there was still the matter of his court-martial. Jenkins arrived at Camp Zama, Japan, on September 11, 2004, where Lt. Col. Paul Nigara was awaiting him. Jenkins, by then 64, greeted him with a salute, saying, “Sir, I’m Sergeant Jenkins and I’m reporting.”
Held accountable for his desertion
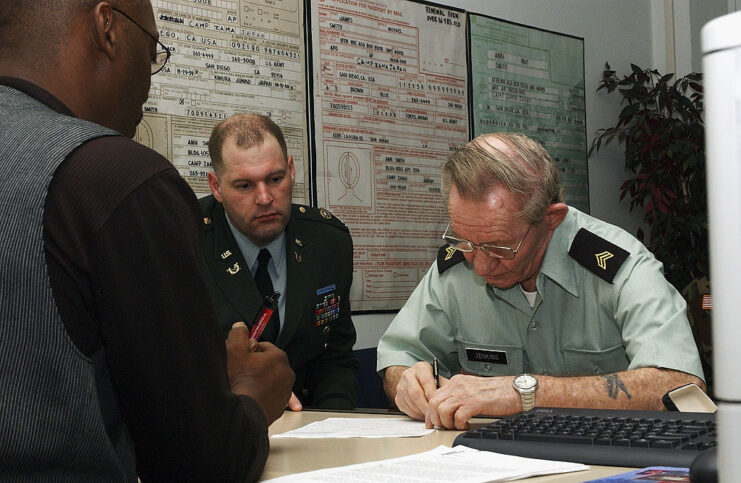

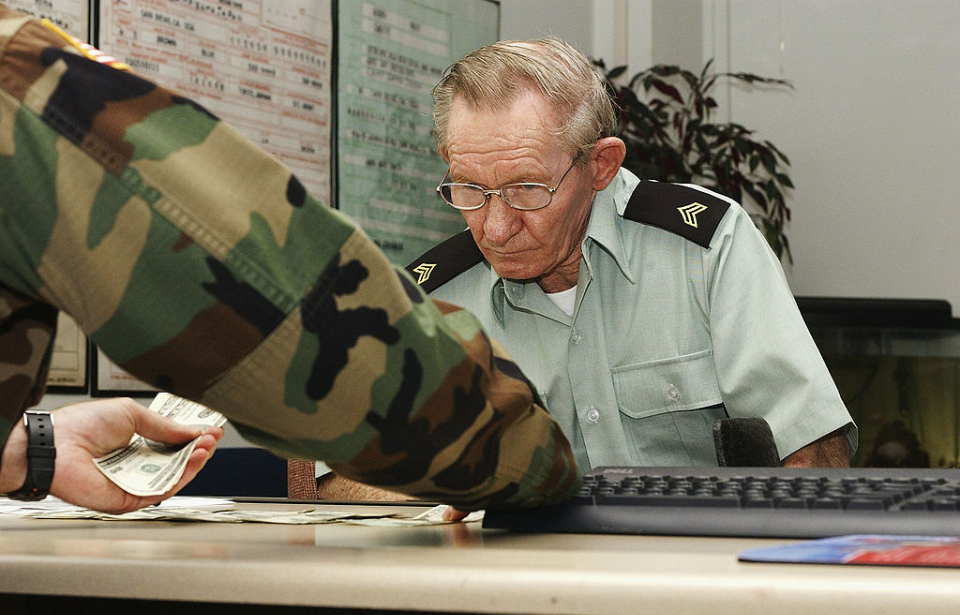
Jenkins’ trial wasn’t held until November 3, 2004. He pleaded guilty to desertion and aiding the enemy by teaching English. He was initially sentenced to six months confinement, but this was later changed to 30 days. The former Army soldier also forfeited all his back pay, was demoted to the rank of private and received a dishonorable discharge.
Despite the ruling, Charles Robert Jenkins was released on good behavior after 25 days. He was reportedly given pay for the time served. In an interview years later, he said that the sentence was “all a big set-up for the outside world so it looked like justice was done.”
Adapting to civilian life
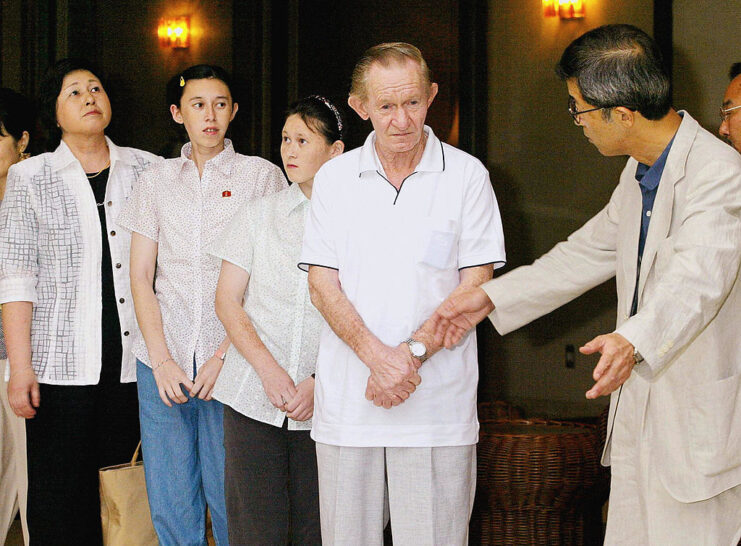

After completing his sentence, Jenkins settled with his family in his wife’s hometown, making a memorable visit to North Carolina to see his to see his aging mother. Despite finally being free from North Korea, he lived with a constant fear that the regime might still come after him. He later shared the details of his extraordinary journey and struggles in his memoir, providing a rare glimpse into his decades-long ordeal.
More from us: National Emergency Command Post Afloat: The ‘Floating White Houses’ for Times of Nuclear War
Jenkins spent his later years as a well-known figure in Japan, where he was granted permanent residency in July 2008. He pursued his love of motorcycling and found work at a local museum during his free time. Jenkins passed away on December 11, 2017, at the age of 77, with cardiovascular disease listed as the cause of death.
