Tanks are designed for front-line combat. These strong armored fighting vehicles are a pivotal part of any land forces in warfare. Tanks can be used in both offensive and defensive situations. With the help of the large-caliber cannon fitted to its rotating turret, the tank can take hold of and dominate an area and prevent the advancement of enemy vehicles during combat. Modern tanks have gone through a century of development from the early armored war vehicles.
The following 10 most bizarre tanks which, among many freakish tank designs, were actually constructed. Some militaries possess bigger dreams than others. However, not surprisingly, most of these ludicrous tanks never saw substantial action in the battlefield.
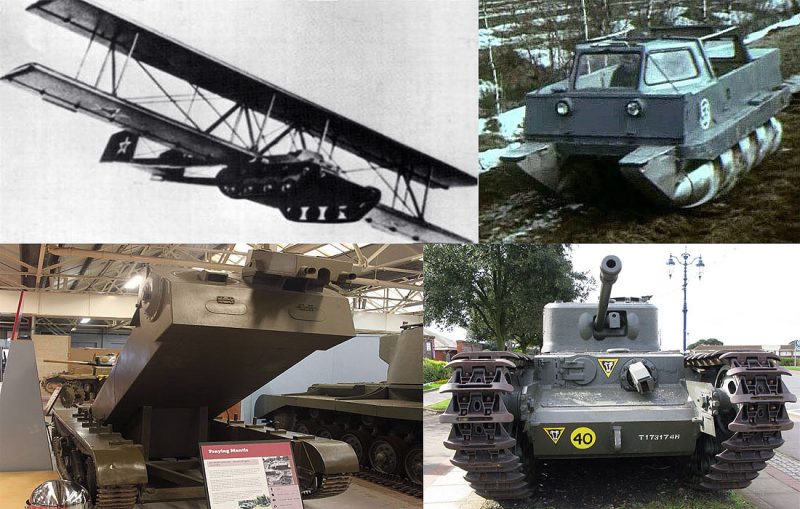
10. Tanks with Wings (1942):
Military strategists have always sought to provide heavy ground support to airborne troops with artilleries and armored vehicles. Soviet Union, Japan and the United Kingdom carried out several partially successful experiments in the 20th century to attach glider wings with tanks so that they could glide into the front line.
Some other nations had loaded light tanks onto gliders to transport tanks into the battlefields. In the 1930s, Soviets strapped T-27 tankettes or tracked armored fighting vehicles underneath heavy bomber aircraft to land them on airfields. Tanks were also experimentally dropped from aircraft with parachutes attached to them or were simply dropped into the water.
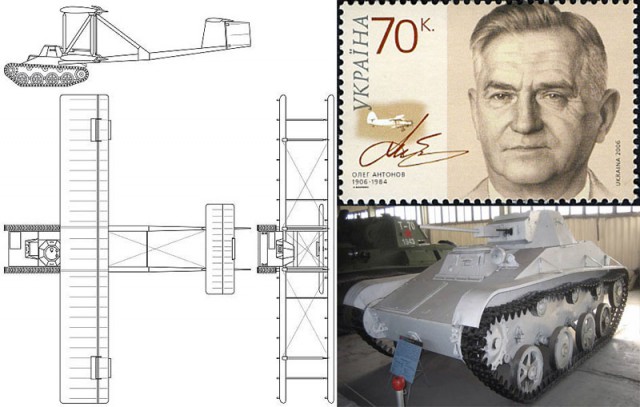
Among many problems with air-dropping vehicles, the main problem was the separate air dropping of crews of the vehicles causing a delay in operation. Gliders allow the crew to reach drop zone along with their armored vehicles also minimize the exposure of the valuable towing aircraft. Soviet aircraft designer Oleg Antonov was ordered by Soviet Air Force to design a glider to land tanks.
But Antonov was ambitious enough to attach a detachable cradle to a T-60 light scout tank. The tank weighed 12,800 pounds. The added framework on the T-60 tanks was capable of bearing wood and fabric biplane wings and a twin tail. Such tanks with wings could glide into the battleground, drop its wing structure and get ready for action within minutes.
One prototype was built in 1942 after removing armament, headlights, ammunition and most of the fuel from the T-60. The winged T-60 was intended to be towed by a Soviet heavy bomber Tupolev TB-3 or Petlyakov Pe-8. Despite reducing the weight of the T-60 tank, the TB-3 bomber was forced to ditch the tank-glider to avoid crashing due to the extreme drag of the T-60 during its only flight on September 2, 1942.
The ‘Antonov A-40’ reportedly glided smoothly, and it was piloted by a Soviet Glider pilot. It landed safely and after detaching the glider, the T-60 was driven back to base. The Antonov A-40 required being towed at 99 mph or 160 kph. Due to lack of aircraft with adequate power to tow the flying tank at the required speed, the project was canceled. But the Soviet efforts continued.
By mid-1970s they became successful in para dropping tracked amphibious fighting vehicle, BMD-1 with its crew aboard. Oleg Antonov became the first chief of Antonov, the world famous aircraft company in Russia and Ukraine in 1946. The company was named so in his honor.
Images Used (Clockwise from left): (1) Schematic of the Soviet tank with glider wing, ‘Antonov A-40‘. (2) Soviet aircraft designer Oleg Antonov illustrated on a stamp of Ukraine. He became chief of aircraft company Antonov in Russia and Ukraine. The company was named so in his honor. (3) A T-60 tank at the Kubinka Tank Museum in Moscow Oblast
Video Used: 3D video illustration of the Russian flying tank Antonov A-40
9. Screw Drive Vehicle or Tank, ZIL-2906 & ZIL-4904 (1960s & 1970s):
Screw-propelled vehicles are specially designed to cope with mud, swamp, snow and ice. These could be land or amphibious vehicles moved by the rotation of one or more drill or screw like cylinders. The first screw-propelled vehicle was designed in the United States in 1868 for agricultural purpose. A screw driven snowmobile called ‘Armstead Snow Motor’ was developed in the 1920s in California.
In 1941, during the WWII, British journalist and inventor Geoffrey Pyke proposed developing a screw-driven war vehicle based on the American Armstead Snow Motor so that the Allies could carry out an offensive against the Nazi occupation of Norway. However, his screw-propelled prototype of the Weasel was rejected by the United States and it was converted into M29 Weasel, a tracked vehicle.
A German soldier wanted to solve the difficulties of tracked vehicles in the deep snow in Russia. So he built a working prototype of screw-propelled snow machine in 1944. But it never went into production. The US Navy produced a Marsh Screw Amphibian in 1969 during Vietnam War.
The Soviets built a screw-propelled amphibious vehicle, the ZIL-2906 in the 1960s. It was used to move through inaccessible areas, such as- Siberia, to recover landed cosmonauts. A bigger screw driven vehicle design called ZIL-4904 was built in the 1970s.
ZIL-4906 or the ‘bluebird’ was made in the 1970s which weighed two and a half ton. It was a 6-wheeled amphibious rescue vehicle, designed to carry the ZIL-2906 and recover the landed Soyuz space craft capsules. ZIL-4904 was the largest screw driven vehicle of all time. A few of these were built and then the project was discarded.
Images Used (Clockwise from top left): (1) ZIL-2906 (2) ZIL-4904 (3) ZIL-4906, the ‘bluebird’ (4) ZIL-2906 in action
8. Bigfoot Tuck or Tank, Bigfoot Fastrax (1987):
The Bigfoot monster trucks were introduced in 1979 in United States by Bob Chandler who established the Bigfoot 4×4 Inc. Monster truck races became popular in the 1980s. The company built and owned many vehicles including Bigfoot Fastrax, which is a monster truck with body style of a 1990 Ford Aerostar, built on the chassis of M48 Patton tank, running on tank treads instead of the usual monster tires.
The upper half of its body is a fiberglass replica of Aerostar. Two Ford 460ci engines and C6 automatic transmissions are used in it. It also has different suspensions than other monster trucks. This Bigfoot Fastrax tank competed on several occasions and is mostly used as a display vehicle at the company’s headquarters in Hazelwood, Missouri.
Image Used: Bigfoot Fastrax at a Monster Truck show
7. Brtish Flame-Throwing Tank, Churchill Crocodile (1943 to 1951):
Churchill Crocodile was a British flame-throwing medium tank produced from October 1943, prior to the Normandy Invasion. It was a variant of the MkIV Churchill IV tanks. British military engineer, Major General Percy Hobart developed this tank. A number of his unusually modified tanks were called Hobart’s Funnies and these were deployed as part of the Invasion of Normandy. These special designs were used to overcome the problems of the invasion and these played an important role in the landings.
A 6.5-ton armored trailer attached to the tank carried the 400 imperial gallons or 1,800l fuel and compressed nitrogen. The trailer was connected with the Crocodile tank by armored coupling and could be jettisoned from within the tank if required. The flame throwing mechanism could produce 80 one second bursts.
Churchill Crocodile was a successful assault weapon that could often force enemy troops to retreat or surrender. It took part in the Battle for Brest in France in 1944 and Operation Clipper in Geilenkirchen, Germany in the same year. Crocodiles also served in Korea until 1951.
Images Used (From left): (1) A Churchill Crocodile firing its flamethrower in August 1944 (2) The armored fuel trailer of the flamethrower of the Crocodile, photographed in 1944
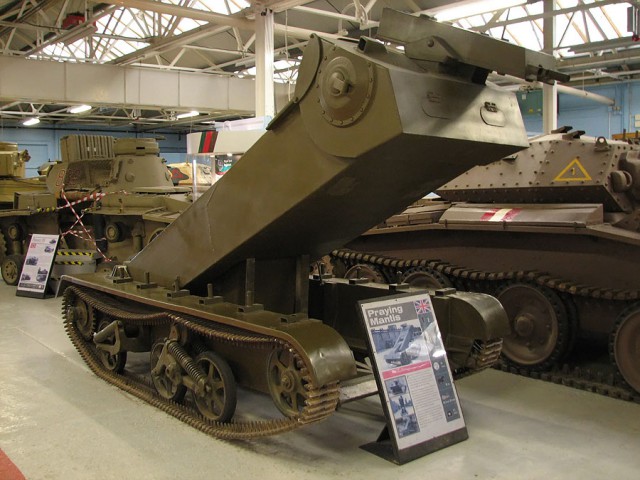
6. Praying Mantis Tank (1943 to 1944):
The Praying Mantis tank was an attempted variant of the Universal Carrier, the British armored tracked vehicle introduced in 1940 for transporting support equipment and personnel. The Mantis was an attempt to produce an armored vehicle that could fire over obstacles. Initially, it was designed to carry just one person.
A two-man version appeared in 1943. An enclosed metal box structure replaced its hull. The box structure is pivoted at the rear of the vehicle and a driver and a gunner lay down in it. The structure could be elevated too and on top of it was a machine gun turret fitted with two Bren light machine guns.
The idea was to drive the Praying Mantis up to hedgerow or a wall, raise the gun and fire over the barrier from a safe position. After trials, it was rejected in 1944. A Praying Mantis survives in the Bovington Tank Museum in Dorset, South West England.
Image Used: The surviving Praying Mantis prototype at Bovington Tank Museum in Dorset, England.
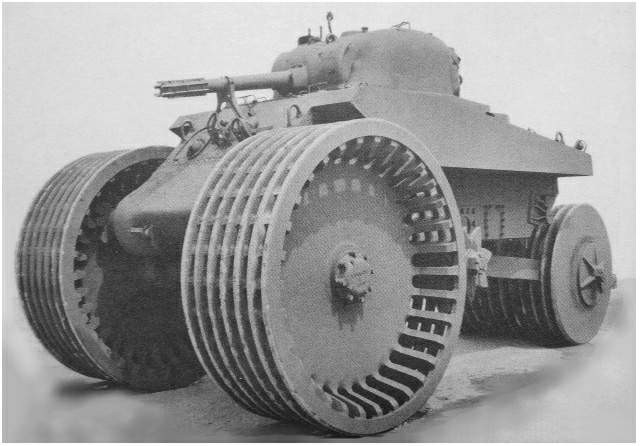
5. Tricycle Tank, Mine Exploder T10 (1944):
M4 Sherman medium tanks were the most numerous battle tanks used by the US and some western allies during WWII. Its productions continued from 1941 to 1945 and 49,234 units were produced. M4 Sherman tank had several variants and there were some M4 Sherman-based vehicles including the Mine Exploder T10. It was a remote controlled unit.
Its underside was thickened with 25mm steel and the sides were adapted to give room for the huge 96-inch wheels. The rear wheel had a diameter of 72 inches. It weighed 116,400 lbs and could attain a maximum speed of 3kmph while clearing mines and 10kmph on a clear road. The T10 was tested in 1944 but was rejected due to its heavy weight and related drawbacks.
Image Used: Mine Exploder T10, the Tricycle Tank
4. Firefighting Tank, Hurricane T-55 (1991-93):
The Soviet T-54 and T-55 tanks have been in service since 1946 until today. 86,000 to 100,000 tanks of the T-54/55 tank series have been produced, making it the most produced tank series in history. As many as 50 countries, official and un-official armed forces have been using T-55 tanks. Hurricane T-55 is a modified version of T-55 built to fight large-scale oil fire. T-55 chassis was used. But its turret was replaced with a MIG-21 jet engine mount and multiple water nozzles.
Fire extinguishing was done in ‘aerosol method’. It worked by finely atomizing water with the help of jet engine. Water was delivered in the exhaust plume of the jet engine. Water became atomized by the exhaust gas stream and it was launched to a long distance. Cooling effect could be achieved in a range of around 100m.
Image Used: A Hurricane T-55 firefighting tank at German Fire Museum at Fulda in Hesse, Germany
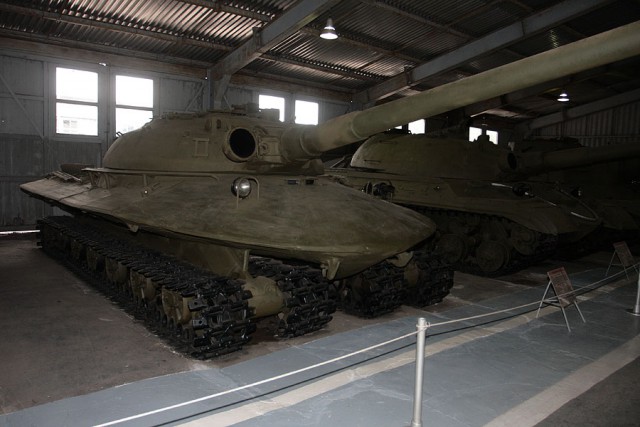
3. Nuclear-Proof Tank, Object 279 (1959):
In the cold war era, Soviet Union built this experimental nuclear explosion proof heavy tank called Object 279 in 1959. It was one of the last Soviet prototypes of heavy tanks before Kruschev banned any tank heavier than 37 tons. Only one unit of Object 279 was built at Kirov Industrial Plant in Leningrad. It weighs 132,277 lbs or 60 metric tons. It had a running gear consisting of four-tracks and a 1000 hp 2DG-8M diesel engine that could power the tank to achieve a speed of 55 kph with an active range of 300 km per refueling.
The hull of Object 279 had 182-319mm thick armor with CBRN or chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear protection. It was also covered by a thin, elliptical shaped shield protecting it against Armor piercing projectiles and shaped charge ammunition. The elliptical shield also protected it from overturning due to shockwaves of possible nuclear explosions.
Image Used: The Object 279 on display at Kubinka Tank Museum in 2009
2. Bridge Tank, Boirault machine (1915):
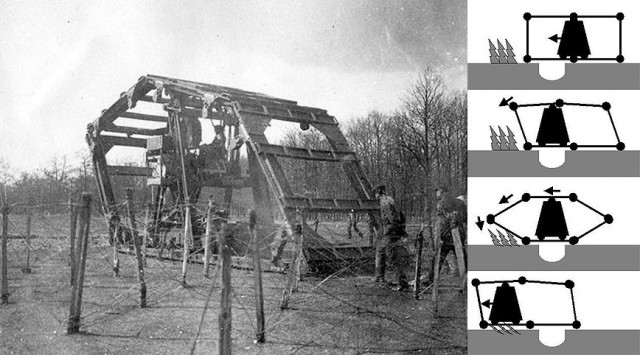
The French experimental landship to drive over the trenches of Western Front during WWI was named after its designer Boirault. It is considered as one of several interesting ancestors of the tank. It was in fact, described as the rhomboid shaped skeleton tank that had a single overhead tank and no armor.
The objective of the Boirault machine was to flatten barbed wired defenses and to ride over trenches and gaps in a battlefield. It was made of huge parallel tracks formed by metallic frames with transverse beams. It was a single track covering the entire width of the machine, rotating around a single triangular center with an 80 hp petrol engine, chains and rods.
Only one unit was built and it had a speed of 3 kph. The project was officially abandoned due to the bridge tank being too fragile and slow. It also couldn’t change direction easily and was nicknamed Diplodocus Militaris after the Diplodocus dinosaur. Within six months of production of this vehicle, the Little Willie prototype of British Mark I tank was developed.
Image Used: A huge rotating frame was used around a motorized center in the Boirault machine
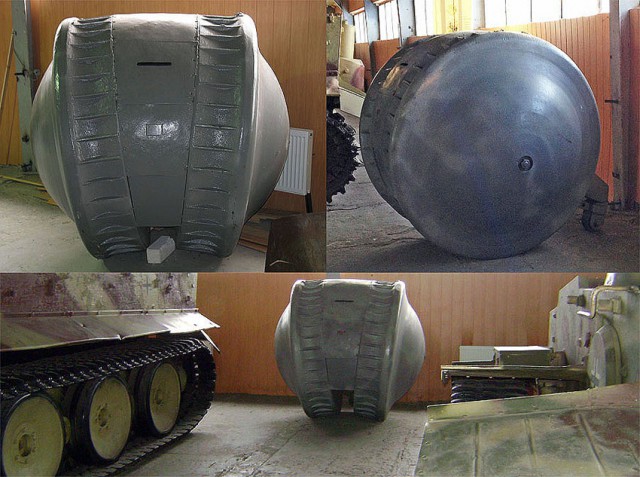
1. Ball Tank, Kugelpanzer (1915):
Kugelpanzer literally means ‘spherical tank’. Built by the Nazis during the WWII, it was a one-man reconnaissance tank prototype with an armored shell and viewpoint. It was one of the most bizarre armored fighting vehicles ever built. One unit could be found today at Kubinka Tank Museum in Russia as part of their collection of German armored vehicles.
The driving mechanism had been removed from the vehicle by the authorities. It is assumed that an engine was mounted behind or under the operator. A small directional wheel was installed at the rear to steer two circular tracks fitted to the sides of the sphere. The Ball Tank might not have been intended to be a platform for offensive weapons.
It could have been possibly used for laying cables during the war. Another rolling armored vehicle prototype was built by Germany earlier during the WWI called ‘Hansa-Lloyd Bremen Treffaswagen’ which reportedly had two guns or a cannon fitted to it.
Images Used (Clockwise from top left): (1) Front view of Kugelpanzer (2) Sideview of Kugelpanzer (3) Size comparison of Kugelpanzer with other tanks
https://youtube.com/watch?v=5PM-XiJ4KIk
Video Used: Documentary on tank warfare during WWI, WWII, Cold War and American tank manufacturing procedure during cold war